03. Signal Properties
Header Text
Signal Properties
In this concept, you will see a general overview of signal properties, including definitions of the wavelength of a signal and the general form for the equation of a signal.
Single Wave Parameters
Wavelength
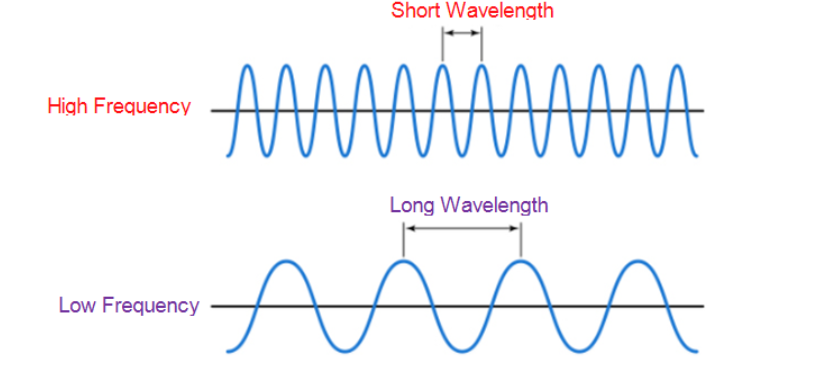
Wavelength ( \lambda ) is the physical length from one point of a wave to the same point on the next wave, and it is calculated as
The higher the frequency the smaller the wavelength.
\]](img/image.png)
Wavelength of a signal
[source: techplayon ]
Frequency, Amplitude
The frequency of a wave is the number of waves that pass by each second, and is measured in Hertz (Hz). The automotive radar generally operates at W band (76GHz - 81GHz). The signal at this frequency is referred to as millimeterWave since the wavelength is in mm.
The Bandwidth of a signal is the difference between the highest and the lowest frequency components in a continous band of frequencies.
The Amplitude is the strength of the signal. Often it corresponds to the power of the RF signal/electromagnetic field defined in dB/dBm. It is relevant while configuring the output power of the radar and sensing the received signal. Higher the amplitude of the Radar signal, more is the visibility of radar. Automotive Radar can operate at max of 55 dBm output power (316 W)
dB, dBm, mW, and W conversions can be found here .
\]](img/image25.png)
Frequency of a signal [ source ]
\]](img/image1.png)
Amplitude of a signal [ source ]
Phase of a Signal
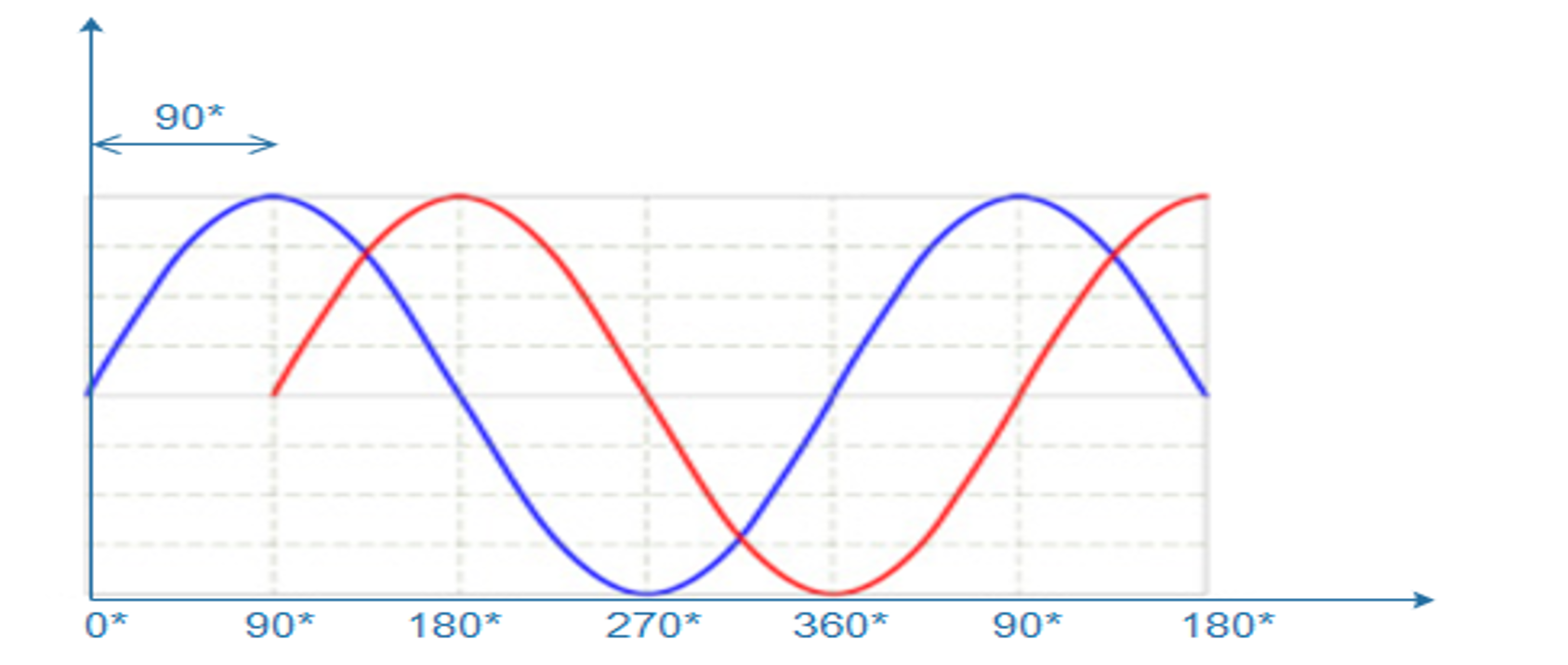
Phase is a particular point in time on the cycle of a waveform, measured as an angle in degrees. A complete cycle is 360°. The phase for each argument value, relative to the start of the cycle, is shown in the image below, in degrees from 0° to 360° and in radians from 0 to 2π.
The frequency can also be defined as the first derivative of the phase with respect to the time.
where
This property will be used in measuring the doppler frequency shift for a moving target.
Phase of sinusoidal waveform
source : Wikipedia
Phase
The difference between the phases of two periodic signals is called the
phase
difference
.
At values of when the difference is zero, the two signals are said to be in phase, otherwise they are out of phase with each other.
The phase information processing is important as we go through doppler processing as well as Angle of Arrival techniques for radar.
Phase
Phase of a signal
General Equation of a Wave
RF signal equation
A wave travelling in space is defined by the following equation:
Below, the variables in the equation are defined:
- A is the amplitude of the signal
- f_c is the signal frequency
- \phi is the phase of the signal